Watch More Solved Questions in Chapter 22. The order of elimination reaction is.
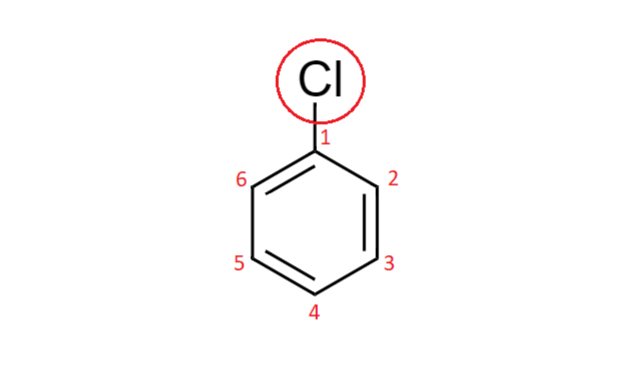
Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides A Chlorob Quizlet
The formation of less stable carbonium ion 2.

. FIGURE CANNOT COPY. In a similar fashion these same metals reduce the carbon-halogen bonds of alkyl halides. Find step-by-step Chemistry solutions and your answer to the following textbook question.
Draw structures for the following molecules. Plan and predict the outcomes of the following chemi-cal reactons. Until the late 1980s alkyl halides called chloro-.
The inductive effect 5. Structural formula for an aryl halide is created by first drawing the aromatic structure and then replacing its hydrogen atoms with the halogen atoms specified as shown in Figure 223a. Video answers for all textbook questions of chapter 22 Substituted Hydrocarbons and Their Reactions Glencoe Chemistry by Numerade.
The carbon atoms here are in a cyclic orientation. Recognize alkyl halides as compared to vinyl and aryl halides c. Mg H20 в NBS A hvheat dry ether.
Cl Br I. 3 o halides C 3 C-X undergo only S N 1 substitution reactions and either E2 or E1. Aryl group is a simple aromatic compound where one hydrogen atom is removed from the ring allowing it to get attached to a carbon chain.
The chemical reactivity of several alkyl halides is based on their structures and functions associated with them. They form a homologous series represented by C n H. The structural formula for an aryl halide is created by first drawing the aromatic structure and then replacing its hydrogen atoms with the halogen atoms specified.
Recognize primary 1 o secondary 2 o and ter-tiary 3 o halides b. The main difference between alkyl and aryl is that alkyl group has no aromatic ring whereas aryl group has an aromatic ring. The common names of alkyl halides are derived by naming the alkyl group followed by the halide.
Recognize C α and C β in an alkyl halide 2. An alkyl halide can be made by starting with an alkene and adding H-X to it. Draw structures for these alkyl and aryl halides.
MAINIDEA Compare and contrast alkyl halides and aryl halides. An alkyl halide A on reaction with magnesium in dry ether followed by treatment with ethanol gave 2-. Chlorobenzene text b.
Define functional group and name the group present in each of the following structures. Draw the structures of the following alkyl halides. Draw all the structures.
Science Chemistry QA Library 1. For the alkyl halides a prefix. Describe and compare the structures of alkyl halides and aryl halides.
12 text -difluoro-3-iodocyclohexane text d. The halogen is converted to halide anion and the carbon bonds to the metal the carbon has carbanionic character. Alkyl halide structures can be classified as primary secondary and tertiary.
Naming Halocarbons Organic molecules containing functional groups are given IUPAC names based on their main-chain alkane structures. 1122 text. 13 text -dibromobenzene text e.
Write the name and draw the structure of the alkyl group that corresponds to 0202. Rob Ronald Alkyl halides are categorized as 1 o 2 o and 3 o which actually refers to the degree of substitution on the carbon bearing the halogen atom. Chem 348 Fall 2012 Organic Chemistry Prof.
Which of these has weakest C CI bond. Cl Cl 1-chloro-2-methylpropane 2R 3R 6S- 2 chloro 8 ethyl 36 dimethyl decane Cl Br Cl I F Br I Br F. On the other hand aryl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms bonded covalently to benzene rings or aromatic groups.
Draw the structures of all the eight structural isomers that have the. Reactivities of Alkyl Halides in Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions Before You Begin. What are possible alkyl halides formed for radical chlorination of ethane.
Name these alkyl groups. Alkyl halides are organic compounds having halogen atoms covalently attached to aliphatic carbon atoms or carbon atoms in a straight hydrocarbon orientation. An aryl group always contains an aromatic ring.
If the compound is an alkyl halide indicate whether it is 1 2 or 3. Name the type of organic compound each substance. Bimolecular nucleophilic substitution S N2 b.
Halide reactivity increases in the order. Classify each halo compound shown below as an alkyl vinyl or aryl halide. The following equations illustrate these reactions for the commonly used metals.
Aryl halides These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is directly. 1 o halides CH 2-X undergo only S N 2 substitution reactions and E2 elimination reactions. Name and write the structures of.
Having learnt the classification of halogenated compounds let us now learn how these are named. 1 text -bromo-4-chlorohexane text c. Connection to Earth Science Alkyl halides are widely used as refrigerants.
In alkyl halides the halogen atom is bonded to an alkyl group R. Name and draw alkyl halides a. The blank lines coming off of the carbons can be either another carbon or a hydrogen but since they are not important.
1 halides by substitution and 2 halides by either or both of the reactions. Mathrmsp2 hybridized carbon attached to halogen a 123 b 245 c 25 d 45. B Aryl halides These are the compounds in which the halogen atom is bonded to the sp2-hybridised carbon atom of an aromatic ring.
Circle any organic halide below that can undergo a S N1 or S N2 type substitution reaction. Longer carbon-halogen bond 4. Give the possible product s may be more than one product in each step for A B and C in the following reactions.
Aryl halides are less reactive towards nucleophilic substitution reactions as compared to alkyl halides due to 1. Since the neutral bonding pattern for halogens is one bond and three lone pairs the carbon and halogen always share a single bond. Identify the nucleophile substrate and leaving group in the general equations for reactions 1 and 2.
And also if it is allylic or benzylic. Draw the structures of all substrates you will be using in this reaction and classify them as 1º 2º 3º aryl benzylic or some combina tion of these such as 1º benzylic. 3 halides 2 halides 1 halides Alkyl halides also undergo ER in the presence of base as Nu Loss of HX and formation of bond H R OR CH2 CH2 Cl ROH CH3CHCH2 Cl CH3 ii In general 3 halides tend to react by elimination.
Give IUPAC names for the following alkyl halides.

Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Equation Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text
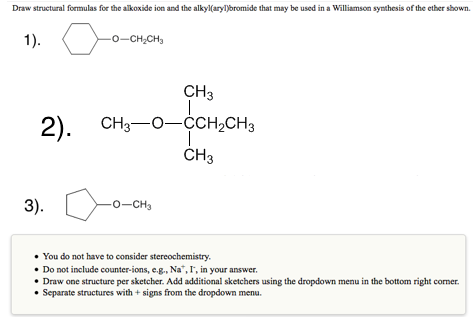
Solved Draw Structural Formulas For The Alkoxide Ion And The Chegg Com
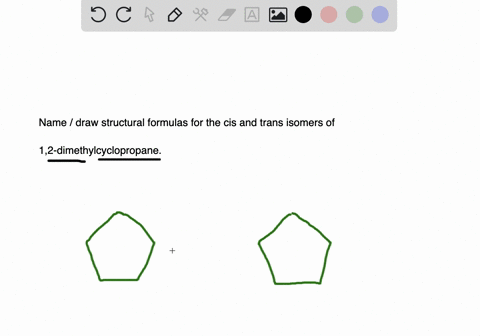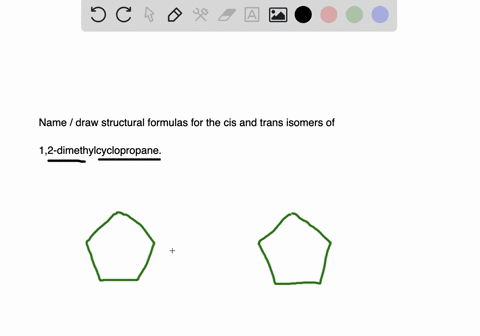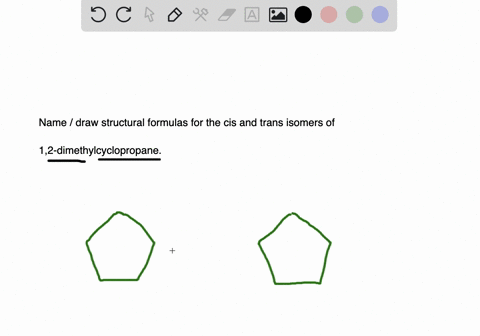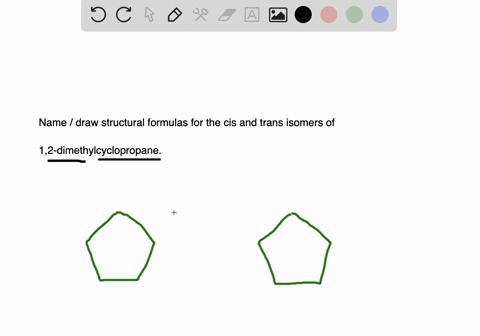
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane

Solved Xex Dx 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Chegg Com
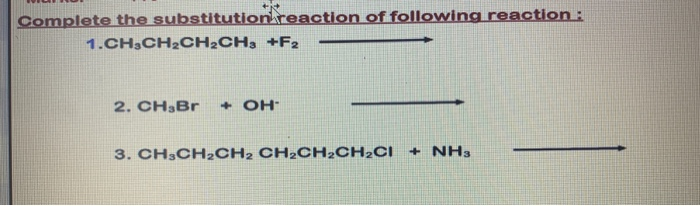
Solved 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Chegg Com

Solved Xex Dx 32 Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Chegg Com
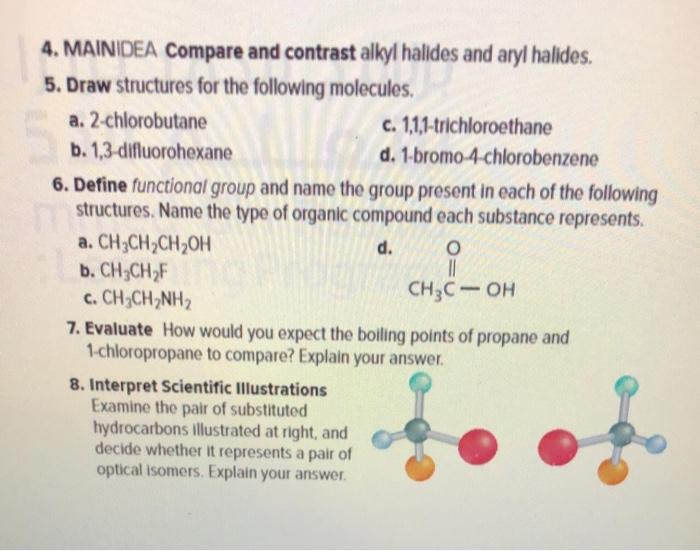
Solved 4 Maindea Compare And Contrast Alkyl Halides And Chegg Com
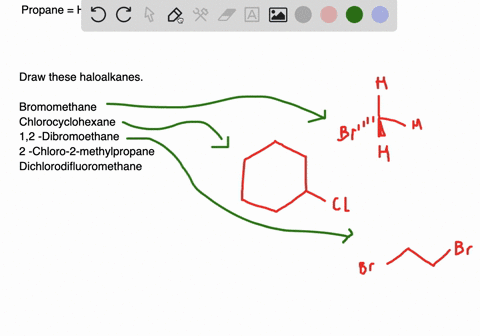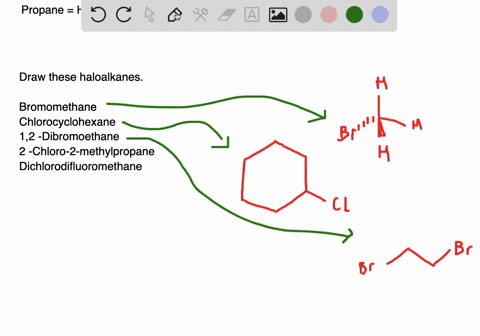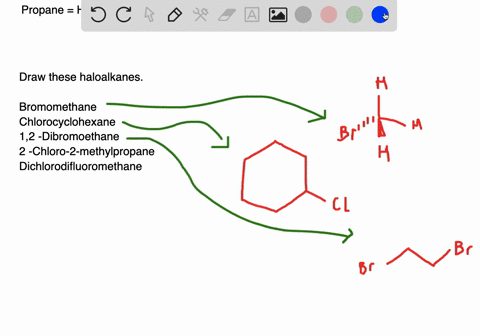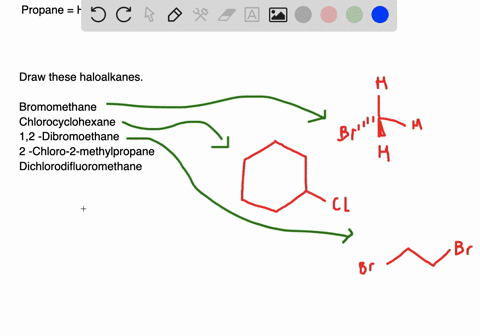
Solved Draw Structures For These Alkyl And Aryl Halides Begin Array L Text A Chlorobenzene Text B 1 Text Bromo 4 Chlorohexane Text C 1 2 Text Difluoro 3 Iodocyclohexane
0 comments
Post a Comment